Introduction
Transfusion: Transfusion word originated from Latin word “transfundere” in 1500 means pouring liquid from one vessel to another vessel and later in 1660s, in medical sense, it is used for “transfer of blood from one person/ animal to another”.
Transfusion is done for symptomatic relief of, or preventing deleterious effect of decrease in constituent of blood, limited to Red Blood Cells or Hemoglobin, White Blood Cells, Platelets, or coagulation factors in form of plasma or concentrated coagulation factors.
As it is true for all medicine, transfusion is also having beneficial or deleterious effect on recipient and also same is true for the blood component donors.
Definition:
Blood Transfusion reaction is defined as an unintended or undesired response to administration (transfusion) of blood component or blood product in blood recipient.
Classification of Blood Transfusion Reaction:
Blood Transfusion reaction is classified in to acute transfusion reaction and delayed transfusion reaction depending upon onset of transfusion reaction within 24 hours or after 24 hours of start of transfusion. These can be further classified in to various category depending upon pathophysiological and clinical presentation.
Figure 1: Types of Blood Transfusion reactions1
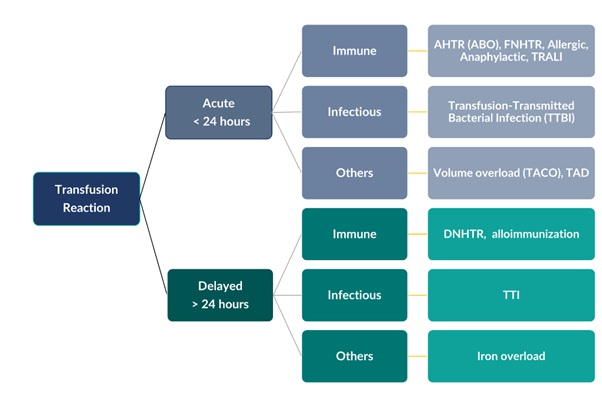
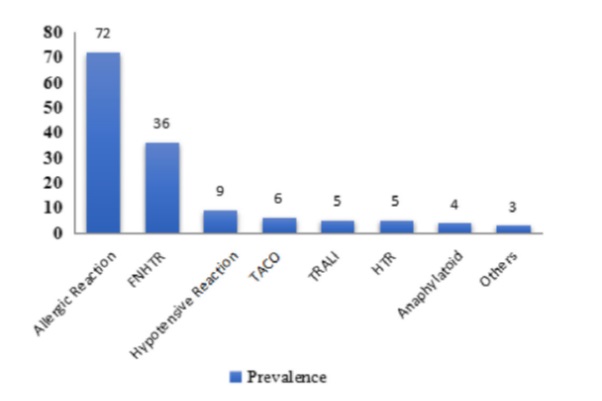
Figure 2: Prevalence of Blood Transfusion Reaction in India between 2011 – 2018, (HvPI)2
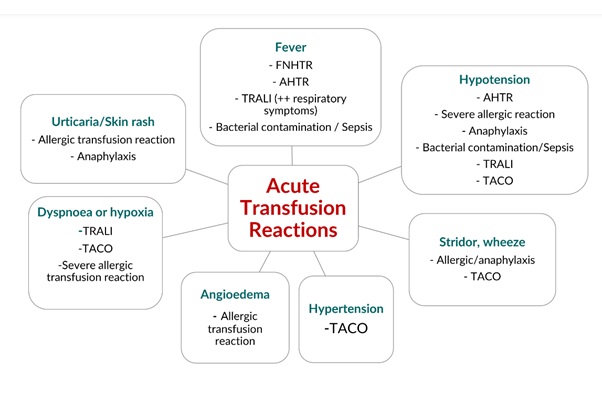
Possible Diagnosis of Acute Blood Transfusion Reaction based on symptoms:
Diagnosis and classification of Blood transfusion reaction is first and most important step in managing it. It can be suspected if initial, and intra or post transfusion vitals and clinical condition of recipients altered, which cannot be explained by underlying medical condition of recipient.
Clinical presentation includes:
Fever: Rise in body temperature > 1 C with or without chills and rigor.
Dyspnoea: sudden and sever shortness of breath & difficulties in breathing.
Hypoxemia: Decrease oxygen saturation (PaO2/ FiO2 < 300 mm Hg or O2 saturation < 90%), not explained by underlying medical condition
Rash/ Urticaria: Irritated and or swollen skin areas
Other Allergic/ Anaphylactic Manifestation: Strider, Wheezing, Angioedema
Hypotension: Decrease in blood pressure more than or equal to 20 mm Hg not related to underlying medical condition or systolic blood pressure below 80 mm Hg
Hypertension: Diastolic blood pressure more than 100 mm Hg or Increase more than or equal to 30 mm Hg systolic blood pressure, not related to underlying medical condition
Tachycardia: Increase heart rate.
Tachypnoea: Increase respiratory rate.
Possible diagnosis can be done based on initial clinical presentations follow:
Figure 3: Possible Diagnosis of Acute Blood Transfusion Reaction1
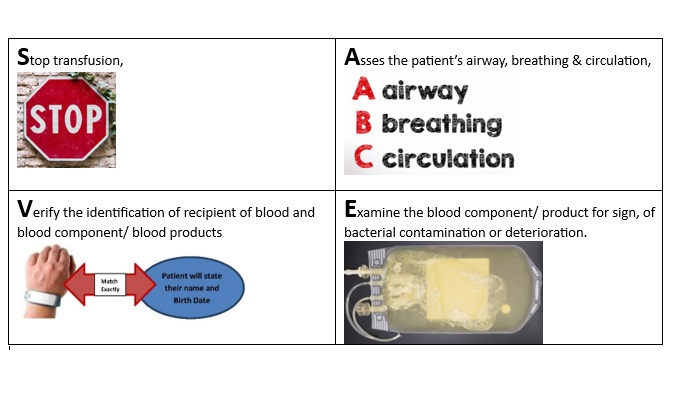
Immediate Action after blood transfusion reaction:
First action to be taken once it is recognized that blood recipient has possible blood transfusion reaction is “SAVE”:
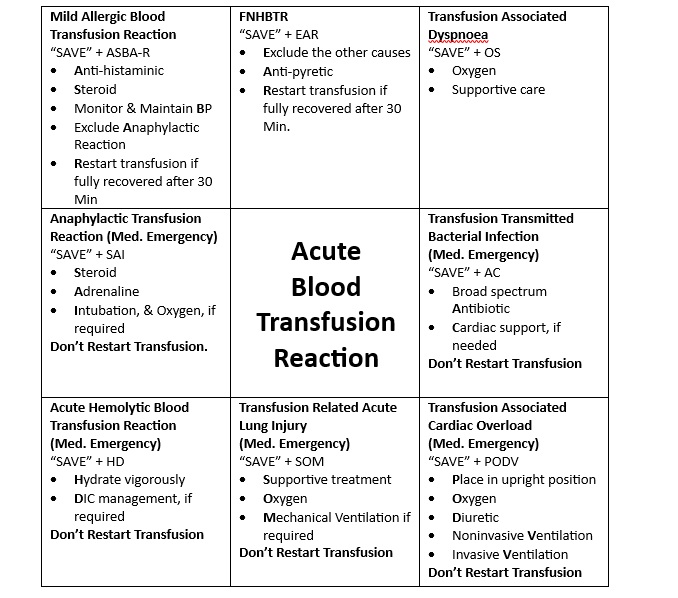
Management of Acute Blood Transfusion Reaction:
Reference:
1: ISBT Transfusion Reaction Module
2: Suryatapa Saha. Deepthi Krishna. Raghuram Prasath. Deepti Sachan. Incidence and Analysis of 7 Years Adverse Transfusion Reaction: A Retrospective Analysis. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus (Jan-Mar 2020) 36(1):149–155

Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!